|
SODIUM BICHROMATE |
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 10588-01-9,
12018-32-5
(Anhydrous) 7789-12-0 (Dihydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 234-190-3 | |
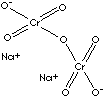
| FORMULA | Na2 Cr2O7· 2H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 297.98 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2841.30.0000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 50 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Dichromic acid disodium aalt dihydrate; 重铬酸钠; | |
| Sodium dichromate dihydrate; Disodium dichromate dihydrate; Sodium dichromate; Natriumdichromat (German); Dicromato de sodio (Spanish); Dichromate de sodium (French); Sodio (dicromato di) (Italian) | ||
|
SMILES |
Cr](O[Cr](=O)(=O)[O-])(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+] | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
EXTRA NOTES |
EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 068304 | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Odorless Orange to Red crystals or granules | |
| MELTING POINT | 357 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
400 C |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.35 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Highly soluble (74.0% at 25°C) |
|
| pH |
3.0 - 4.6 upon concentration |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | 10 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 4; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 2; Special Hazard: OX | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
400 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Sodium dichromate PubChem Compound Summary - Sodium dichromate IPCS INCHEM - Chromium KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Chromate http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Dichromate http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Sodium dichromate Local: Potassium dichromate, also called red potassium chromate, is a bright yellowish-red crystals melting point at 396 C, decomposes at 500 C. Sodium dichromate is a red to orange deliquescent crystals melts at 320C. Sodium dichromate undergoes hydration when heated at 105C. They are soluble in water, insoluble in alcohol. Sodium and potassium dichromates are widely used as sources of other chromium compounds including chromic acid. Dichromates are power oxidizing agents which find applications in:
In biological field, potassium dichromate is used as a fixative for used for conservation of tissue sections. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Odorless orange crystal grain | |
| Na2Cr2O7· 2H2O | 98.0% min | |
| SULPHATES | 0.4% max | |
| CHLORIDES |
0.2% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: I) | |
| UN NO. | 3086 | |
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
|
|
|
GHS |
|
|
| SIGNAL WORD |
Danger |
|
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H272-H301-H312-H314-H317-H330-H334-H340-H350-H360FD-H372-H410 |
|
|
P STATEMENTS |
P201-P220-P260-P273-P280-P284 |
|
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
45-46-60-61-8-21-25-26-34-42/43-48/23-50/53 |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
53-45-60-61 |
|
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
||